What Is NBR Rubber?
Overview of Oil-Resistant NBR Rubber (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber)
-
What Is NBR Rubber?
NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber) is a synthetic rubber created through the copolymerization of acrylonitrile and butadiene. It is renowned for its excellent resistance to oil, solvents, and various chemicals, making it widely used in industrial applications.

OIL-RESISTANT RUBBER TIGER-JAPAN
-
Chemical Composition
-
Acrylonitrile (ACN): Enhances oil and solvent resistance. ACN content typically ranges from 18% to 50%:
-
High ACN content → Better oil resistance but reduced elasticity.
-
Low ACN content → Better elasticity but lower oil resistance.
-
-
Butadiene: Provides elasticity, abrasion resistance, and flexibility.
-
Characteristics of NBR Rubber
-
Excellent resistance to oils and solvents, especially mineral oils, engine oils, and fuels.
-
Good abrasion, tear resistance, and mechanical strength.
-
Temperature resistance from −40°C to around 120°C (depending on formulation).
-
Good water resistance but not durable in ozone, UV, and harsh weather environments.
-
Properties can be adjusted by varying ACN content or adding specific additives.
-
Applications of NBR Rubber
-
Automotive Industry:
-
Gaskets, seals, fuel and oil hoses.
-
Sealing components for hydraulic oil systems.
-
-
Oil and Gas Industry:
-
Oil-resistant rubber hoses, gaskets in oil pumps.
-
-
Glove Manufacturing:
-
Protective gloves, chemical-resistant medical gloves.
-
-
Machinery Components:
-
Oil-resistant seals, gaskets, fuel hoses.
-
-
Consumer Products:
-
Rubber pads, oil-resistant footwear.
-
-
Limitations of NBR Rubber
-
Poor resistance to sunlight, UV rays, and ozone.
-
Not resistant to strong acids or aggressive solvents like ketones and esters.
-
Can harden and become brittle when exposed to excessive heat for prolonged periods.
-
Comparison Between NBR and Other Rubber Types
| Property | NBR (Nitrile Rubber) | NR (Natural Rubber) | EPDM | Silicone |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil Resistance | Very Good | Poor | Poor | Moderate |
| Temperature Range | −40°C to 120°C | −50°C to 80°C | −50°C to 150°C | −60°C to 250°C |
| Elasticity | Moderate | Very Good | Good | Moderate |
| Chemical Resistance | Good (Oils, Solvents) | Poor | Very Good (Chemicals, Ozone) | Very Good |
| Ozone & Weather Resistance | Poor | Moderate | Very Good | Very Good |
| Mechanical Strength | Good | Very Good | Moderate | Moderate |
-
NBR Variants
-
XNBR (Carboxylated NBR): Offers enhanced abrasion resistance and mechanical strength.
-
HNBR (Hydrogenated NBR): Improved resistance to heat, ozone, and chemicals.
-
Summary
NBR rubber is an ideal material for applications requiring oil, solvent, abrasion, and moderate temperature resistance. However, it should be protected from sunlight, ozone, and strong chemicals to maintain long service life.
Contact: PHUC MINH ENGINERING CO., LTD. for trusted, high-quality oil-resistant rubber products.
Email: info@pm-e.vn
Cellphone/Zalo: +84907450506 / +84902720814
Address: 92/38, Street No. 12, Quater 18, Binh Hung Hoa Ward, Binh Tan District, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam.
Related News

FDA-Approved Rubber Gaskets – Safe Solutions for Food & Medical Applications
23/04/2025
FDA-Approved Rubber Gaskets – Safe Solutions for Food & Medical Applications Phuc Minh Engineering Co., Ltd. is proud to be one of the leading distributors in Vietnam of rubber gaskets for food and medical applications. Our products are made from high-quality materials and meet the strict FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) standards – ensuring safety for direct contact with food and medical equipment.
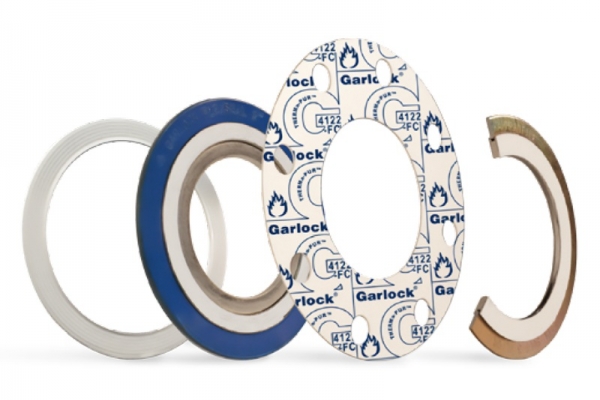

HIGH-TEMPERATURE GASKETS – UP TO 1000°C WITH THERMa-PUR™ 4122 MATERIAL
23/04/2025
HIGH-TEMPERATURE GASKETS – UP TO 1000°C WITH THERMa-PUR™ 4122 MATERIAL In many heavy industries such as chemical processing, oil refining, cement, and power generation, sealing materials must endure extreme temperatures, high pressure, and harsh oxidative environments. Phuc Minh Engineering Co., Ltd. is proud to be a distributor of high-temperature gaskets rated up to 1000°C, combining Garlock’s advanced THERMa-PUR™ 4122 material with Corrugated Metal Gaskets (CMG) – delivering an optimal sealing solution for extreme industrial conditions.

Trusted Industrial Valve Distributor – Industry Leader
26/02/2025
With the continuous growth of Vietnam's economy, the demand for industrial valves and related technical solutions has significantly increased. In this article, we would like to introduce a reputable and leading industrial valve distributor in this field — Phuc Minh Engineering Co., Ltd.

Top 10 best water flow meter brands today
12/02/2025
Sensus water flow meter: Origin: Germany. Advantages: The product has high precision, durable design and stable operation in many different environmental conditions. Sensus clocks are certified by European CO, CQ, suitable for large-scale projects.
What Is a Breather Valve?
05/02/2025
A breather valve, also known as a pressure-vacuum relief valve (PVRV), is a safety device that protects storage tanks from explosion or collapse caused by pressure differences. It is typically installed on top of storage tanks for fuels, chemicals, LPG, or gases.
















.png)






