2.Principal Applications for Steam
Steam is used in a wide range of industries. Common applications for steam are, for example, steam heated processes in plants and factories and steam driven turbines in electric power plants, but the uses of steam in industry extend far beyond this.
Here are some typical applications for steam in industry:
- Heating/Sterilization
- Propulsion/Drive
- Motive
- Atomization
- Cleaning
- Moisturization
- Humidification
In the sections that follow, we will discuss various types of applications for steam, and provide some examples of steam-using equipment to illustrate them.
Steam for Heating
Positive Pressure Steam
Steam is typically generated and distributed at a positive pressure. In most cases, this means that it is supplied to equipment at pressures above 0 MPaG (0 psig) and temperatures higher than 100°C (212°F).
Heating applications for positive pressure steam can be found in food processing factories, refineries, and chemical plants to name a few. Saturated steam is used as the heating source for process fluid heat exchangers, reboilers, reactors, combustion air preheaters, and other types of heat transfer equipment.
| Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger |
|---|

|
In a heat exchanger, steam raises the temperature of the product by heat transfer, after which it turns into condensate and is discharged through a steam trap.
| Steam Oven |
|---|

|
Superheated steam heated to 200 – 800°C (392 - 1472°F) at atmospheric pressure is particularly easy to handle, and is used in the household steam ovens seen on the market today.
Vacuum Steam
The use of steam for heating at temperatures below 100°C (212°F), traditionally the temperature range in which hot water is used, has grown rapidly in recent years.
When vacuum saturated steam is used in the same manner as positive pressure saturated steam, the temperature of the steam can be quickly changed by adjusting the pressure, making it possible to achieve precise temperature control unlike applications using hot water. However, a vacuum pump must be used in conjunction with the equipment, because merely reducing the pressure will not drop it to below atmospheric pressure.
| Heating with Latent (Steam) Heat |
|---|
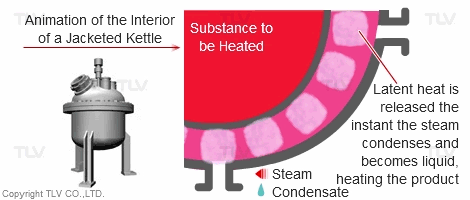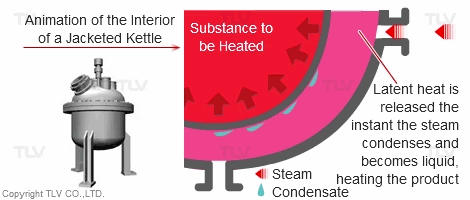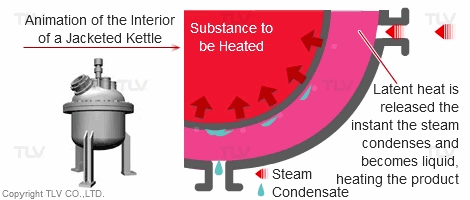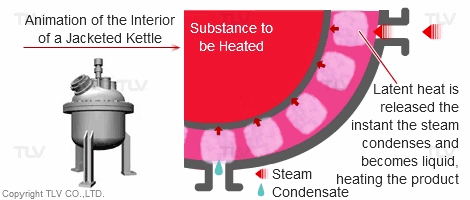
|
Compared with a hot water heating system, this system offers fast, even heating. The set temperature is rapidly reached without causing unevenness in temperature.
Steam for Propulsion/Drive
Steam is regularly used for propulsion (as a driving force) in applications such as steam turbines. The steam turbine is a piece of equipment that is essential for the generation of electricity in thermal electric power plants. In an effort to improve efficiency, progress is being made toward the use of steam at ever-higher pressures and temperatures. There are some thermal electric power plants that use 25 MPa abs (3625 psia), 610°C (1130°F) superheated, supercritical pressure steam in their turbines.
Superheated steam is often used in steam turbines to prevent damage to equipment caused by the inflow of condensate. In certain types of nuclear power plants, however, the use of high temperature steam must be avoided, as it would cause problems with the material used in the turbine equipment. Instead, high pressure saturated steam is typically used. Where saturated steam must be used, separators are often installed in the supply piping to remove entrained condensate from the steam flow.
Besides power generation, other typical propulsion/drive applications are usually for either turbine-driven compressors or pumps, ex. gas compressors, cooling tower pumps, etc
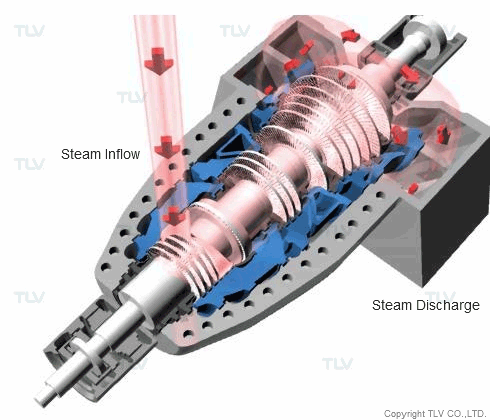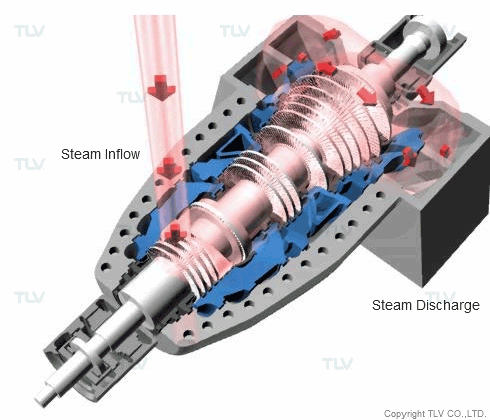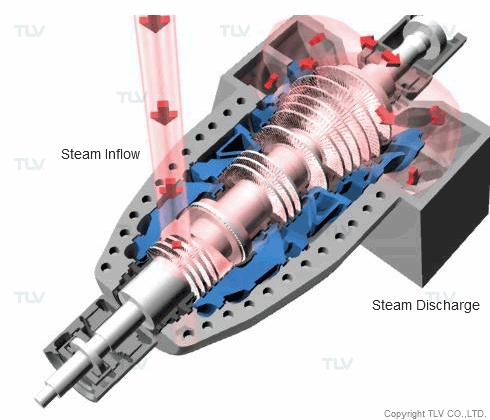
The driving force from the steam causes the fins to turn, which then causes the rotor on the attached power generator to rotate, and this rotation generates electricity.
Steam as Motive Fluid
Steam can also be used as a direct “motive” force to move liquid and gas streams in piping. Steam jet ejectors are used to pull vacuum on process equipment such as distillation towers to separate and purify process vapor streams. They are also used for continuous removal of air from surface condensers, in order to maintain desired vacuum pressure on condensing (vacuum) turbines.
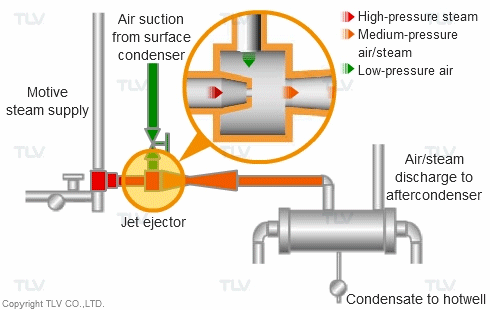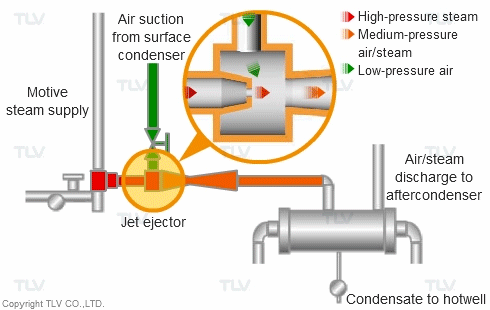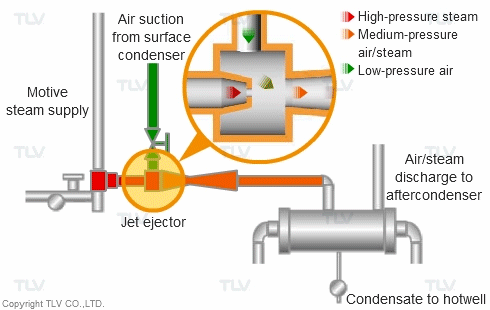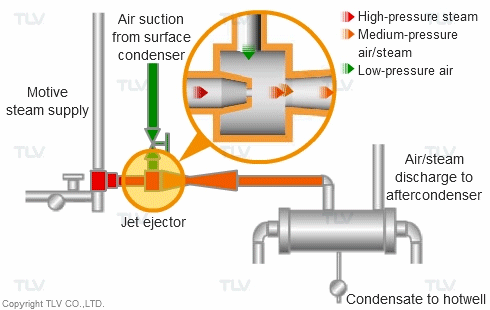
High pressure motive steam enters the jet ejector through the inlet nozzle and is then diffused. This creates a low pressure zone which entrains air from the surface condenser.
In a similar type of application, steam is also the primary motive fluid for secondary pressure drainers, which are used for pumping condensate from vented receiver tanks, flash vessels, or steam equipment that experiences stall conditions.
Steam for Atomization
Steam atomization is a process where steam is used to mechanically separate a fluid. In some burners, for example, steam is injected into the fuel in order to maximize combustion efficiency and minimize the production of hydrocarbons (soot). Steam boilers and generators that use fuel oil will use this method to break up the viscous oil into smaller droplets to allow for more efficient combustion. Flares also commonly use steam atomization to reduce pollutants in the exhaust.
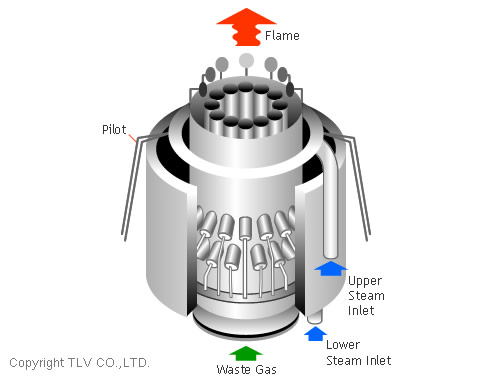
In flares, steam is often mixed in with the waste gas before combustion.
Steam for Cleaning
Steam is used to clean a wide range of surfaces. One such example from industry is the use of steam in soot blowers. Boilers that use oil or coal as the fuel source must be equipped with soot blowers for cyclic cleaning of the furnace walls and removing combusted deposits from convection surfaces to maintain boiler capacity, efficiency, and reliability.
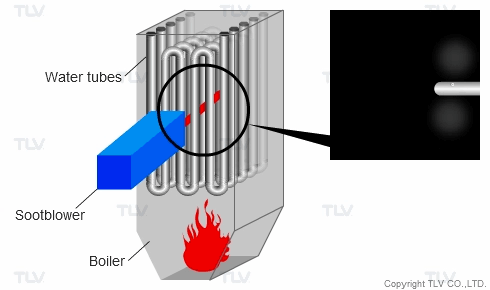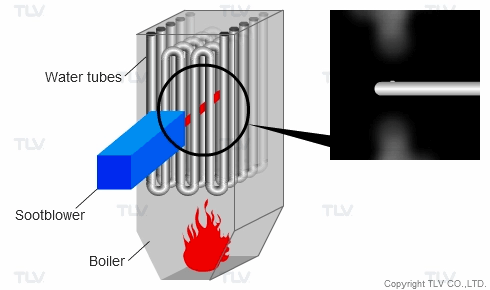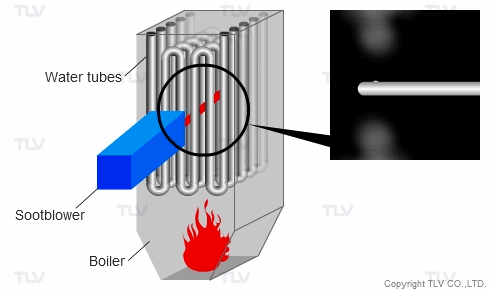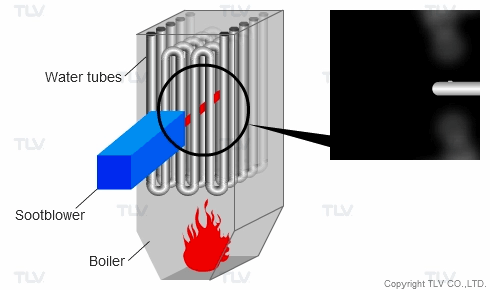
Steam released out of the soot blower nozzle dislodges the dry or sintered ash and slag, which then fall into hoppers or are carried out with the combusted gasses.
Steam for Moisturization
Steam is sometimes used to add moisture to a process while at the same time supplying heat. For example, steam is used for moisturization in the production of paper, so that paper moving over rolls at high speed does not suffer microscopic breaks or tears. Another example is pellet mills. Often mills that produce animal feed in pellet form use direct-injected steam to both heat and provide additional water content to the feed material in the conditioner section of the mill.
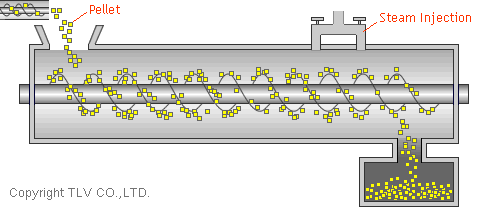
The moisturizing of the feed softens the feed and partially gelatinizes the starch content of the ingredients, resulting in firmer pellets.
Steam for Humidification
Many large commercial and industrial facilities, especially in colder climates, use low pressure saturated steam as the predominant heat source for indoor seasonal heating. HVAC coils, often combined with steam humidifiers, are the equipment used for conditioning the air for indoor comfort, preservation of books and records, and infection control. When the cold air is heated by the steam coils, the relative humidity of the air drops, and it must then be adjusted to normal levels with addition of a controlled injection of dry saturated steam into the downstream air flow.
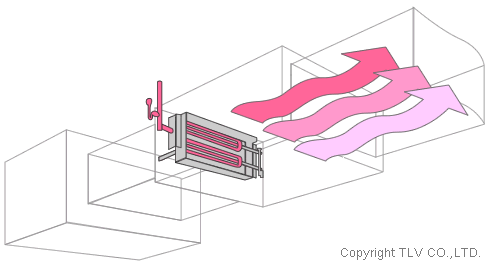
Steam is used to humidify air within an air duct before the air is distributed to other regions of a building.
Related News
Overview of G7 Industrial Valves
14/05/2024
G7 industrial valve is the general term for industrial valves manufactured by countries belonging to the G7 group, including the United States, Canada, England, France, Germany, Italy, and Japan. These valves are known for their high quality, reliability and durability in diverse industrial applications. Below is an overview of the main characteristics of the G7 industrial valve:
What is an industrial valve?
25/04/2024
What is an industrial valve? Industrial Valves are mechanical devices used in pipeline systems in industrial production environments, used to regulate and control the flow of fluid through the pipeline. Industrial valves are manufactured in a variety of designs and types, depending on the medium used, installation location and actual valve usage needs. IWISU distributes genuine imported industrial valves to the market at the most competitive prices, helping customers experience and use the best quality valves on the market.
Consulting and supplying high quality Saigon industrial valves
11/10/2023
Are you looking for a reliable partner in providing and consulting on industrial valves in Saigon? Phuc Minh Company is proud to be a reliable address for all needs of valves and industrial equipment. With many years of experience in the industry, we are committed to bringing you optimal solutions and high quality products.
How much does an industrial valve cost? Guide to choosing the right price
11/10/2023
One of the important challenges when looking to buy industrial valves is knowing the right price and choosing the right product for your specific needs. This article will help you better understand the issue "How much do industrial valves cost?" and provide guidance on choosing the right price.
Learn about leading and reputable industrial valve companies
11/10/2023
In industry, industrial valves play an indispensable role in controlling the flow of liquids, gases, and steam in production and management systems. To ensure safety, performance and compliance with technical and environmental standards, choosing leading and reputable industrial valve companies is an important decision.
















.png)






